 Aditya L1
Photo Courtesy: UNI
Aditya L1
Photo Courtesy: UNI
Aditya-L1 begins collecting scientific data at distances greater than 50,000 km from Earth
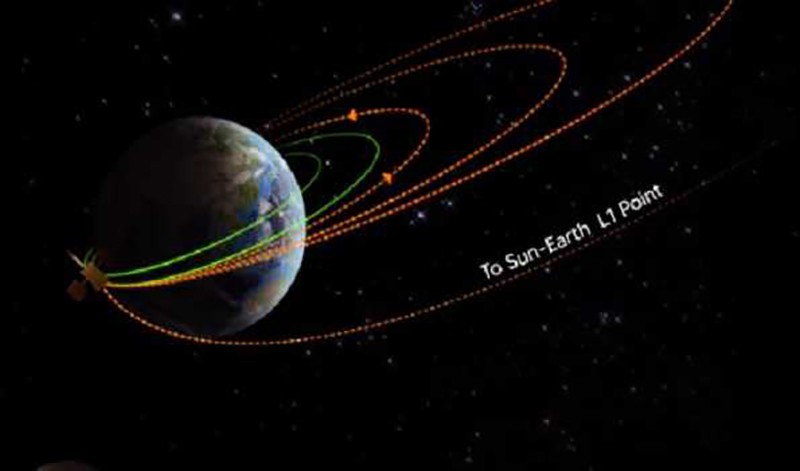
India's first Solar exploratory mission Aditya-L1 to study the Sun, has commenced collecting scientific data at distances greater than 50,0000 km from Earth.
The sensors of the STEPS instrument have begun measuring supra-thermal and energetic ions and electrons at distances greater than 50,000 km from Earth, ISRO said on Monday, in a Mission update.
This data helps scientists analyze the behaviour of particles surrounding Earth.
ISRO posed on X : "Aditya-L1 has commenced collecting scientific data."
"The sensors of the STEPS instrument have begun measuring supra-thermal and energetic ions and electrons at distances greater than 50,000 km from Earth," it said.
"This data helps scientists analyze the behaviour of particles surrounding Earth," it added.
ISRO also released a graphical figure that displays variations in the energetic particle environment, collected by one of the units.
"It showed variation in integrated counts over time recorded by one of the STEPS Sensors on September 10, 2023," ISRO said.
The Supra Thermal & Energetic Particle Spectrometer (STEPS) instrument, a part of the Aditya Solar Wind Particle EXperiment (ASPEX) payload, has begun collection of scientific data.
STEPS comprises six sensors, each observing in different directions and measuring supra-thermal and energetic ions ranging from 20 keV/nucleon to 5 MeV/nucleon, in addition to electrons exceeding 1 MeV.
These measurements are conducted using low and high-energy particle spectrometers.
The data collected during Earth’s orbits helps scientists to analyse the behaviour of particles surrounding the Earth, especially in the presence of the magnetic field of Earth.
STEPS was activated on September 10, 2023, at a distance greater than 50,000 km from Earth. This distance is equivalent to more than eight times the Earth's radius, placing it well beyond Earth's radiation belt region.
After completing the necessary instrument health checks, data collection continued until the spacecraft had moved farther than 50,000 km from Earth.
Each unit of STEPS is operating within normal parameters.
A figure displays measurements depicting variations in the energetic particle environment within Earth's magnetosphere, collected by one of the units. These STEPS measurements will persist during the cruise phase of the Aditya-L1 mission as it progresses towards the Sun-Earth L1 point.
They will continue once the spacecraft is positioned in its intended orbit and the data collected around L1 would provide insights into the origin, acceleration and anisotropy of solar wind and space weather phenomena.
STEPS was developed by the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) with support from the Space Application Centre (SAC) in Ahmedabad.
(With UNI inputs)
Top Headlines
-
News
Sona College student Team Nexus AI designs an intelligent PLC programming assistant
March 08, 2026
-
News
'Guest of India struck in international waters': Iran furious after US submarine torpedoes IRIS Dena
March 05, 2026
-
News
Ali Khamenei (19392026): Irans Supreme Leader who ruled with an iron grip
March 01, 2026
-
News
Ali Khamenei (19392026): Irans Supreme Leader who ruled with an iron grip
March 01, 2026
-
News
Ayatollah Ali Khamenei killed in US-Israeli Air Strikes; Irans Revolutionary Guards vow sweeping retaliation
March 01, 2026
-
News
PM Modi expresses displeasure over NCERT judiciary chapter, wants accountability fixed
February 26, 2026
-
News
Former New Zealand PM Jacinda Ardern to relocate to Australia amid growing Kiwi exodus
February 26, 2026
-
News
Major aviation boost for Kashmir: Cabinet clears development of a new Civil Enclave at Srinagar International Airport
February 24, 2026
-
News
India urges all nationals to leave Iran 'by available means' as US-Iran tension grows
February 23, 2026
-
News
Ind.AI: Sovereignty, jobs, energy and the What If?
February 20, 2026





